Vitiligo is a skin disorder characterized by the loss of pigmentation, resulting in white patches on the skin. It occurs when melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin, are destroyed or become dysfunctional. While the exact cause of vitiligo is still unknown, researchers have been exploring various treatment options to manage this condition effectively. One such option gaining attention is the role of omega-3 fatty acids in the treatment of vitiligo. In this article, we will delve into the potential benefits of omega-3 and its mechanism of action in vitiligo management.
Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of polyunsaturated fats that are commonly found in fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, as well as in walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds. They are renowned for their numerous health benefits, including reducing inflammation, supporting heart health, and promoting brain function. In recent years, researchers have turned their focus toward the potential role of omega-3 in dermatological conditions, including vitiligo.

Omega-3 fatty acids have been found to possess anti-inflammatory properties, which can be beneficial for individuals with vitiligo. Inflammation is thought to play a role in the development and progression of vitiligo, and by reducing inflammation, omega-3 fatty acids may help in managing the condition. In addition, omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to modulate the immune system, which is believed to be involved in the destruction of melanocytes in vitiligo.
A study published in the Journal of Dermatological Treatment in 2017 examined the effect of omega-3 fatty acid supplementation on vitiligo patients. The study included 30 participants who were divided into two groups: one group received omega-3 supplementation, while the other group received a placebo. The results of the study showed that the group receiving omega-3 supplementation experienced a significant decrease in the size and progression of vitiligo patches compared to the placebo group. This suggests that omega-3 fatty acids may have a positive impact on the course of vitiligo.
Another study published in the Indian Journal of Dermatology in 2019 investigated the effect of omega-3 fatty acids combined with topical corticosteroids in the treatment of vitiligo. The study included 50 participants who were divided into two groups: one group received omega-3 supplementation and topical corticosteroids, while the other group received only topical corticosteroids. The results demonstrated that the group receiving omega-3 supplementation in addition to topical corticosteroids had better repigmentation of the skin compared to the group receiving corticosteroids alone. This suggests that omega-3 fatty acids may enhance the effectiveness of conventional treatment methods for vitiligo.
The exact mechanism by which omega-3 fatty acids exert their beneficial effects in vitiligo is not yet fully understood. However, it is believed that their anti-inflammatory properties and their ability to modulate the immune system play a significant role. Omega-3 fatty acids have been found to reduce the production of pro-inflammatory molecules, such as cytokines, and increase the production of anti-inflammatory molecules, such as prostaglandins. This anti-inflammatory effect may help to control the inflammatory response associated with vitiligo and prevent further damage to melanocytes.
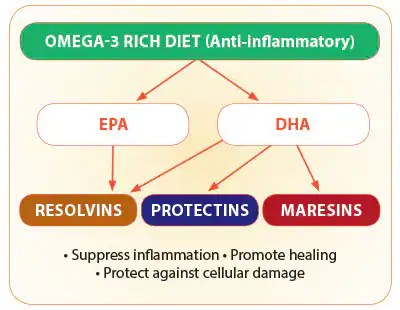
Furthermore, omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to promote the production of eicosanoids, which are lipid signaling molecules involved in various physiological processes, including immune response and inflammation. By promoting the production of specific eicosanoids, omega-3 fatty acids may help to restore the balance within the immune system and prevent the immune-mediated destruction of melanocytes in vitiligo.
While the research on the role of omega-3 in vitiligo is promising, it is important to note that it should not be considered a standalone treatment. Omega-3 fatty acids should be viewed as a complementary approach to be used in conjunction with conventional therapies prescribed by dermatologists.
In addition to omega-3 supplementation, a healthy and balanced diet is crucial for overall skin health. Including foods rich in antioxidants, such as fruits and vegetables, can provide essential nutrients that support the healing process. Moreover, maintaining a well-functioning immune system through regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep can also contribute to managing vitiligo effectively.
It is advisable for individuals considering omega-3 supplementation to consult with a healthcare professional, particularly a dermatologist or a nutritionist, to determine the appropriate dosage and duration of treatment. They can assess the individual’s specific condition and recommend a tailored approach.
While omega-3 fatty acids are generally safe for consumption, it is important to be aware of potential side effects or interactions with medications. Individuals with bleeding disorders or those taking blood-thinning medications should exercise caution and consult their healthcare provider before starting omega-3 supplementation.
In conclusion, the role of omega-3 fatty acids in managing vitiligo shows promise based on the available research. Their anti-inflammatory properties and immune-modulating effects may contribute to the improvement of vitiligo symptoms. However, further studies are needed to fully understand the mechanism of action and to establish standardized guidelines for their use in vitiligo treatment.
Turmeric
Another nutrient that has been shown to have an anti-inflammatory effect AND can help with re-pigmentation through similar mechanisms as omega 3s is turmeric. You are especially likely to benefit from turmeric’s potent action if you tend to suffer from stiff and painful joints. If this is the case, I recommend you check out my colleagues’ write up and try out their Curcumin Gold by clicking here.