Osteoporosis, often referred to as the “silent disease,” is a common and potentially debilitating condition that weakens bones, making them fragile and prone to fractures. This condition affects millions of people worldwide, particularly older adults, and can lead to pain, loss of mobility, and a diminished quality of life. Fortunately, there are proactive steps individuals can take to prevent osteoporosis and maintain strong, healthy bones throughout their lives. In this article, we will explore what osteoporosis is, its risk factors, and practical strategies for its prevention.
Understanding Osteoporosis
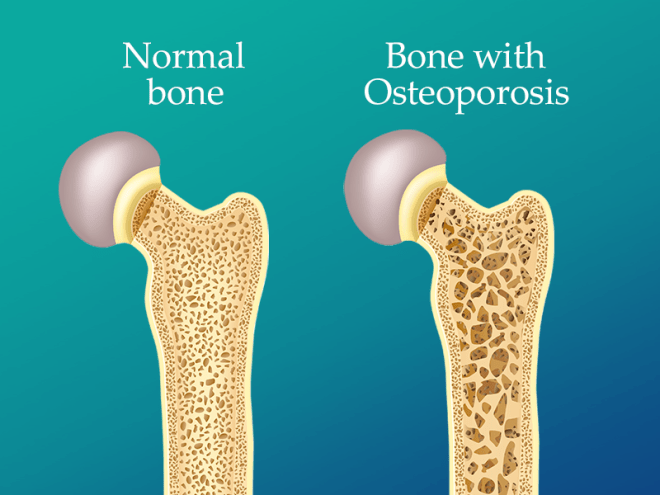
Osteoporosis is a bone disease characterized by the loss of bone density and strength. It occurs when the creation of new bone tissue does not keep up with the removal of old bone tissue. As a result, bones become porous and fragile, increasing the risk of fractures, even from minor falls or bumps. While osteoporosis can affect any bone in the body, fractures in the hip, spine, and wrist are most common.
Risk Factors for Osteoporosis
Several factors can increase the risk of developing osteoporosis, including:
- Age: The risk of osteoporosis increases with age, particularly after the age of 50.
- Gender: Women are more susceptible to osteoporosis than men, primarily due to hormonal changes during menopause that accelerate bone loss.
- Family history: A family history of osteoporosis or fractures may increase your risk.
- Hormone levels: Low estrogen levels in women and low testosterone levels in men are associated with bone loss.
- Diet: Inadequate intake of calcium and vitamin D can weaken bones.
- Physical activity: A sedentary lifestyle contributes to bone loss. Weight-bearing exercises like walking, running, and resistance training help maintain bone density.
- Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption: Both habits can weaken bones.
- Medications and medical conditions: Some medications, such as corticosteroids and certain medical conditions like celiac disease and rheumatoid arthritis, can increase the risk of osteoporosis.
Preventing Osteoporosis
Prevention is the key to maintaining strong bones and reducing the risk of osteoporosis. Here are some practical steps to help prevent this condition:
- Adequate Nutrition: Ensure your diet includes sufficient calcium and vitamin D. Dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods are excellent sources of calcium, while sunlight and supplements can provide vitamin D.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in weight-bearing exercises like walking, jogging, dancing, or weightlifting. These activities stimulate bone growth and help maintain bone density.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption, as both can weaken bones.
- Bone Density Testing: Discuss bone density testing with your healthcare provider, especially if you have risk factors. Early detection can lead to timely intervention.
- Medication: In some cases, medication may be prescribed to prevent or treat osteoporosis. Consult your healthcare provider to determine if this is necessary for you.
- Fall Prevention: Take measures to prevent falls, such as removing tripping hazards at home, using handrails, and wearing appropriate footwear.
- Balanced Diet: Maintain a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrients necessary for bone health, including protein, magnesium, and vitamin K.
- Hormone Therapy: For postmenopausal women, hormone therapy may be an option to discuss with a healthcare provider.
If you are interested in a step-by-step guide on reversing osteoporosis, check out this revolutionary system: The Bone Density Solution (TM)
